Normal pregnancies
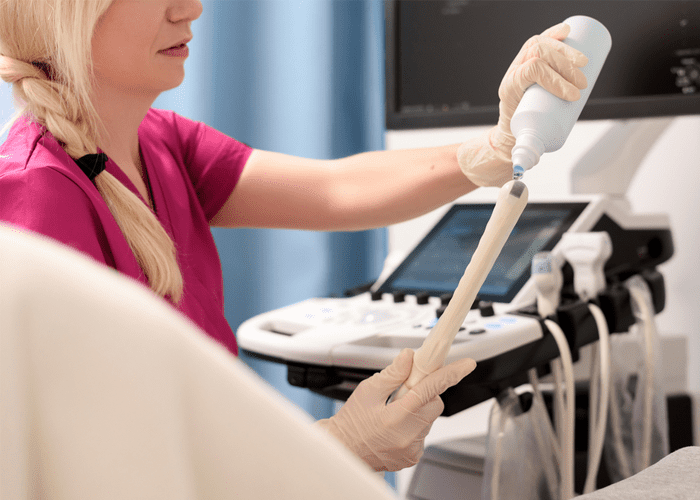
Antinatal and Pelvic USG

Vaginal Birth After Cesarean Section
You could be able to deliver your next baby vaginally if you’ve already undergone a caesarean birth (also known as c-section). After a cesarean delivery, this is known as a vaginal birth (also called VBAC). Cesarean birth is a surgical procedure in which your baby is delivered via an incision made in your belly and uterus. More than 6 to 8 out of ten women (60-80%) who attempt VBAC succeed in delivering their baby. Excessive bleeding, infection, and blood clotting in one or more deep veins in the body are related with successful VBAC (deep vein thrombosis). VBAC may also reduce the risk of hysterectomy (uterus removal) and harm to abdominal organs including the bladder or intestines.
Late pregnancies

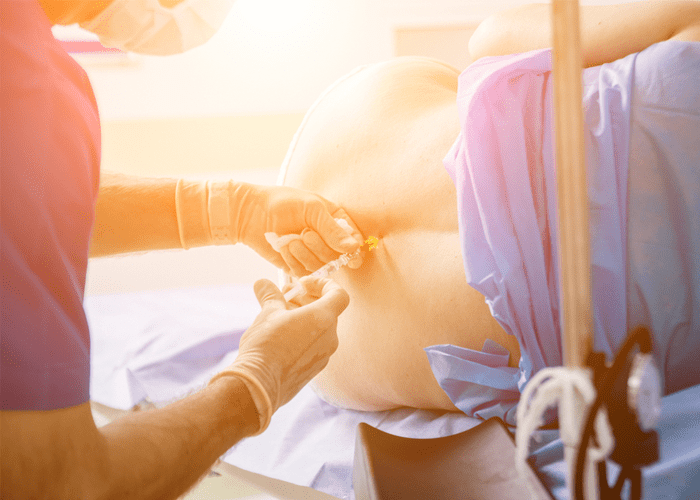
Painless deliveries
An epidural injection provided by an anaesthesiologist for pain management during labour is referred to as a painless birth. It is injected into the lower back, and a plastic tube is inserted around the spinal cord via which medications are distributed. It takes around 10-15 minutes for the medicine to take action. This is a great choice for women who are unable to withstand discomfort and would otherwise have a C-section. Women who had a painless delivery have a better probability of having a natural childbirth with little intervention. It has aided in reducing the number of elective C-sections performed in India. It makes it easier for the baby to descend by relaxing the pelvic and vaginal muscles.
Comprehensive treatment for fibroids

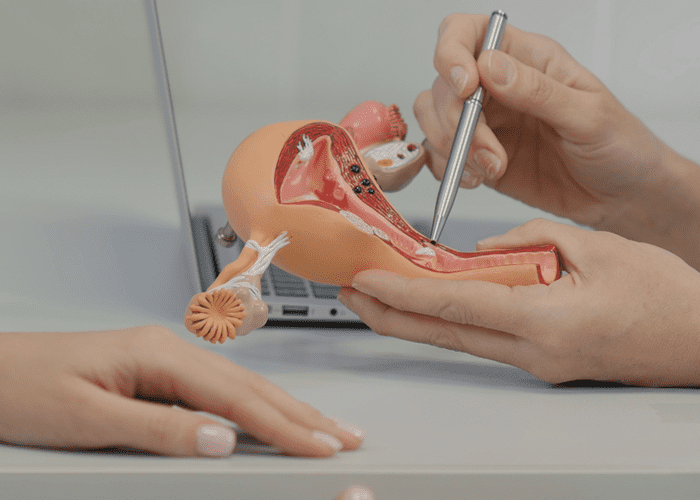
Abdominal hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a medical surgery that removes the complete uterus or the section of the uterus above the cervix. It’s a typical gynecological surgery treatment. The cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other adjacent tissues may also be removed. Pelvic discomfort, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, fibroids, endometriosis, and heavy periods are among illnesses that can be treated by a hysterectomy. The uterus is accessed through an incision in the abdomen during an abdominal hysterectomy.
Vaginal hysterectomy
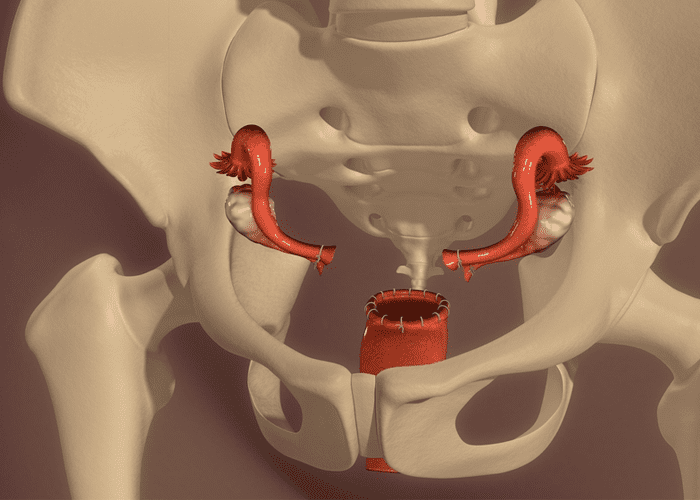

Myomectomies
Hysteroscopy
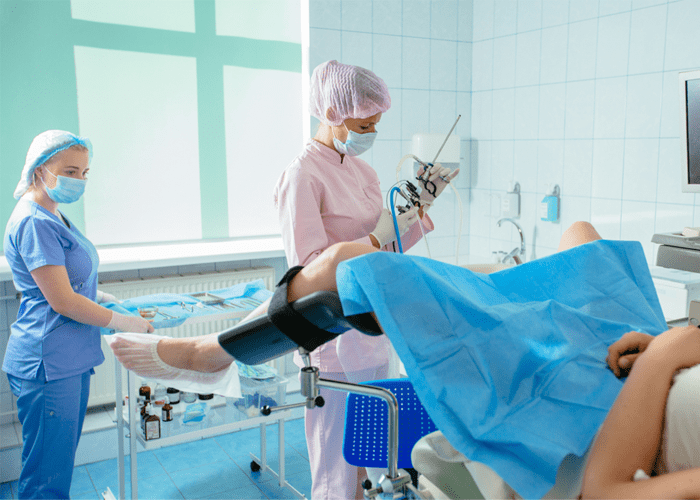

High risk pregnancy care
Intra-Uterine Insemination (IUI)


Pap Smear
Laparoscopic Sterilization
Laparoscopic sterilisation is a technique that offers long-term birth control. The fallopian tubes are either blocked or removed during this procedure, which prevents future pregnancies. The recovery time for this surgery is quite brief. Laparoscopic sterilisation is a surgical treatment that gives women permanent reproductive control. The fallopian tubes are obstructed or removed during female sterilisation.

Antenatal and Postnatal Exercise
Antenatal exercise, which includes joint stretching and muscle strengthening, seeks to avoid low back discomfort and improve physical and psychological preparation for birth. Mothers gain weight, ligaments and joints relax, and abdominal muscles stretch during pregnancy. It takes some time for the body to return to normal after birth. Postpartum workouts will help you regain body form, tone up a sagging abdominal muscle, and avoid low back discomfort. After a normal birth, mothers can begin postnatal exercise 24 hours later.
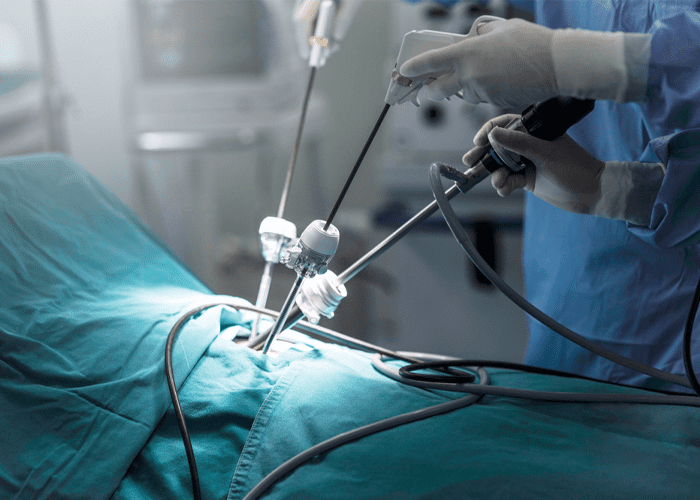
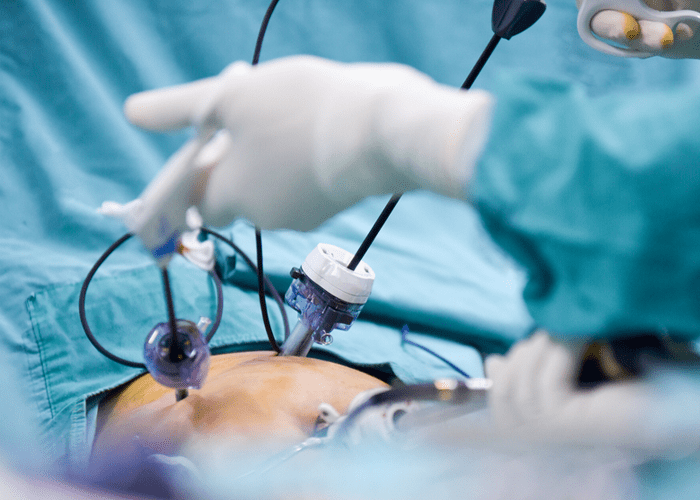
Laparoscopic Surgery (Obs & Gyn)
Gynecological laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that allows the surgeon to operate without making a major incision. A laparoscope is a narrow, illuminated tube with a camera on the end that is introduced into the belly through a tiny incision. The camera transmits images of the inside of the body to a TV display in the operating room, allowing the surgeon to view and operate on the pelvic organs without the need for a large incision.
In the belly, other small incisions may be created to implant very fine specialist surgical equipment. Less discomfort, fewer issues, less scarring, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery are some of the advantages of laparoscopic gynecological surgery versus open abdominal surgery.